160911 Determination of wind loads. Allowable stress design ASD method Comparing FM 128 and ASCE 705 10 16 ExampleA manufacturing building Risk Category II is located in New.
FM Global Wind uplift.
. Following is an overview of the roofing-specific changes. ASCE 716 and its impact on roof system designs June 18 2018. When using FM Globals Loss Prevention Data Sheet 1-28 Wind Design going from enclosed to partially enclosed adds approximately 30 to the wind loads.
Allowable stress design has different load factors Under the new ASCE 7-10 wind specification two things have happened. Versions of referenced standards are found in Chapter 35. Look no further than FM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheets.
However these loads can diverge higher from ASCE 7 if the building is over. EXAMPLE CALCULATION USING ASCE 7-16. This data sheet is intended to be used in conjunction with Data Sheet 1-28 Wind.
ASCE 7-05 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures. Building has a roof slope of ½ inch per foot building height of 40 width 100 and length of 200 with no parapet. Sources to determine wind loads.
Yes I have worked with FM global criteria and can confirm that they are more conservative. One key change relates to roof zone dimensions to align with the ASCE 7-16 Design Standards. FM Global Wind uplift.
Mehta and James M. Required to Meet FM Data Sheets 1-28 and 1-29. They incorporate nearly 200 years of property loss experience research and engineering results as well as input from.
The wind loads will vary in the corners perimeter and field of the roof. FM Global Design Wind Loads are determined by using FM Global Property Loss Preventio n Data Sheets 1-28. Guide to the Use of the Wind Load Provisions of ASCE 7-02 by.
Determining FM Global De sign Wind Loads. When the wind design criteria is transferred between designers for the same project specially between the Engineer of Record and Specialty Engineers it is recommended that reference ASCESEI 7. In their view any building worth insuring by FM is clearly an essential facility.
Wind loads determined per Data Sheet 1-28 are generally approximately 10 greater than those determined by using ASCE 7. Wind LRFD load combination 10W 372 psf. Wind ASD load combination 06W 223 psf.
The stated scope of the revised Data Sheet 1-29. Would require an FM Approved Class 1-60 system design and follow the. FM Global Loss Prevention Data Sheet 1-28 Wind Loads.
Wind resistance Design wind loads FM Approvals or UL ASCE 716 classification or engineering analysis 5 6. Relating ASCESEI 7-10 Design Wind Loads to Fenestration Product Ratings is a technical bulletin jointly endorsed by AAMA Window and Door Manufacturers Association WDMA Fenestration Manufacturers Association FMA and the Door and Access Systems Manufacturers Association DASMAThe bulletin available free for download summarizes information about current. Wind loads on every building or structure shall be determined in accordance with Chapters 26 to 30 of ASCE 7 Its worth noting that the version ie year of publication of ASCE 7 is not specified in the body of the code.
FM 1-28 is intended to provide designers with general guidance for highly protected FM Global-insured buildings. Per Code Section 6141 the minimum wind load for MWFRS shall not be less than 10 psf. The lack of continuity created confusion driving specifiers to rely on.
Look no further than FM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheets. This data sheet provides recommendations for the proper design and installation of above-deck roof components. In some cases depending on the roof dimensions building height and roof slopes four zones.
26 FM Global updated its Property Loss Prevention Data Sheet 1-28 Wind Design to reflect changes in its wind load determination methodology. These load factors are for strength design. 1 The basic _____ to determine wind loads can be located in Figure 261-1 of ASCE 7-16 or shown here in Figure 1.
There are three common methods in the roofing industry used to determine wind loads. Design Wind Speed is 3-second gust speed at 10m with 50 year return period. The traditional load factor which accompanies wind is 16 so a combination which includes dead load live load and wind might be 12 Dead 16 Wind 10 Live.
ASCE 7-02 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures. The wind loads will vary in the corners perimeter and field of the roof. The project must meet the design criteria for the structure outlined in the FM Global Loss Prevention Data Sheet 1-28.
FM 1-28 Summary Update This Code Alert document summarizes changes made to the FM 1-28 Property Loss Prevention Data Sheet dated February 2020. Wind LRFD load combination 16W 350 psf. 45 288 -385 391 -524 Notes.
Loss Prevention Data Sheet 1-28 Wind Design provides the background on the math in calculating the pressures as well as the wind maps. These exacting standards help you reduce the chance of property loss due to fire weather conditions and failure of electrical or mechanical equipment. American Society of Civil Engineers 2005.
Calculation of wind loads for low slope roofing. Outline for determining wind loads from ASCE 7-16. Yes the FM charts use a 115 importance factor.
They incorporate nearly 200 years of property loss experience research and engineering results as well as input from. Glass99 Structural 12 May 14 1730. These exacting standards help you reduce the chance of property loss due to fire weather conditions and failure of electrical or mechanical equipment.
These and other factors are used in conjunction with FM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheet 1-28 titled Design Wind Loads to establish the uplift forces on the specific building. 1-28 titled Design Wind Loads to establish the uplift forces on the specific building. Would require an FM Approved Class 1-60 system design and follow the requirements of data sheet 1-29 for corner and perimeter enhancements.
Wind Loads by ASCE 7-16 and 7-10 Similar Process. Design Wind Speed is 3-second gust speed at 10m with 50 year return period. If the project requires adherence to the full provisions outlined in FMs Data Sheet 1-28 Wind Design and 1-29 Roof Deck Securement and Above-Deck Roof Components the following approach may be followed.
This document provides the necessary data when read in conjunction with the. Items covered include roof covers insulation vapor retarders fasteners and recover assemblies.
Ibc And Fm What S The Difference When It Comes To Wind Design
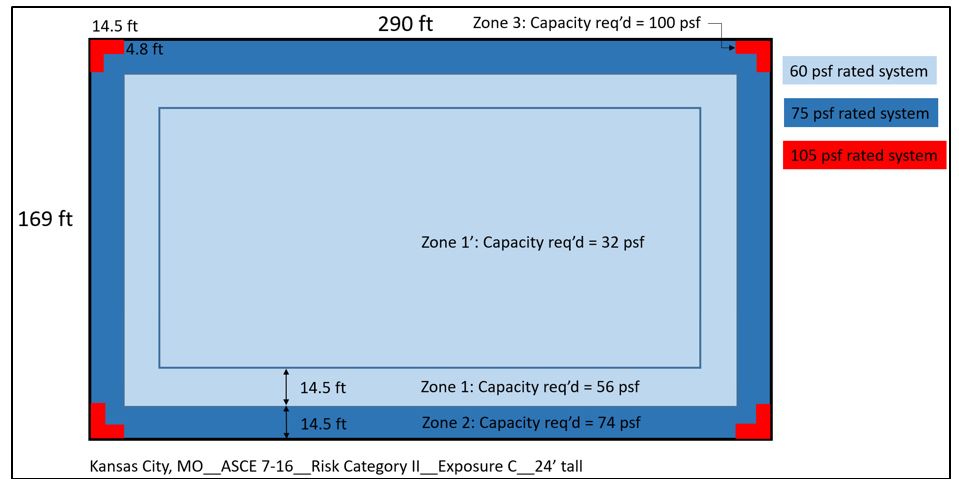
Ceu Wind Design For Roof Systems And Asce 7 2021 06 01 Building Enclosure
Ibc And Fm What S The Difference When It Comes To Wind Design

Understanding Wind Resistant Design Professional Roofing Magazine

Ceu Wind Design For Roof Systems And Asce 7 2021 06 01 Building Enclosure

Comparing Fm 1 28 To Asce 7 10 Professional Roofing Magazine
0 comments
Post a Comment